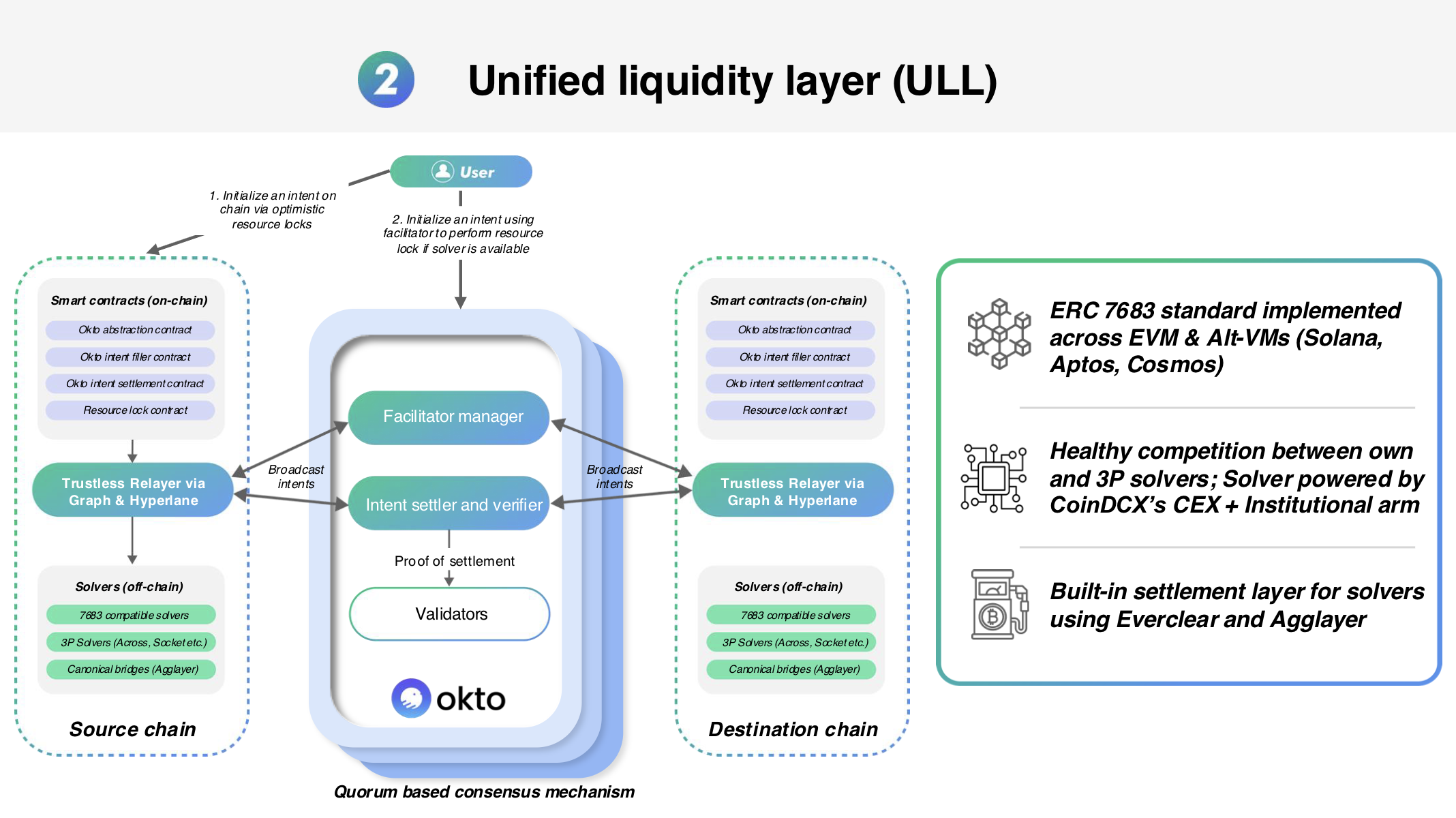
Unified Liquidity Layer (ULL)
The Unified Liquidity Layer (ULL) is a crucial component of the Okto Platform, designed to address liquidity fragmentation across the Web3 landscape. ULL acts as an "aggregator of aggregators," routing cross-chain swaps and transfers through the most efficient and cost-effective pathways available, using an intent-based approach built on the ERC-7683 standard.
Core Concepts
Intent-Based Execution
Instead of users or applications dictating the specific steps (bridge selection, swaps) for a cross-chain transfer, they declare their desired end state, or "intent."
- User Intent: A signed message specifying the desired outcome, e.g., "Swap X Token A on Chain 1 for a minimum of Y Token B on Chain 2, by [deadline]."
- Fulfillment: Off-chain actors, called Fillers (or Solvers), are liquidity providers who monitor these intents. They compete to execute the user's desired transaction, providing the necessary assets on the destination chain.
This model hides the underlying process complexity from the user and allows Fillers to optimize liquidity usage.
ERC-7683 Standard
ULL's design incorporates the ERC-7683 standard. This standard provides common interfaces and logic for cross-chain intent systems. Using this standard helps ULL:
- Promote Interoperability: Allows ULL to potentially interact with other systems following the same standard.
- Standardize Operations: Creates a consistent way to define intents, prove fulfillment, and manage settlement across chains.
ULL Architecture & Components
ULL comprises interconnected on-chain smart contracts and off-chain services working together to enable seamless cross-chain operations:
On-Chain Contracts (Deployed per supported chain)
The ULL relies on two primary smart contracts deployed on each supported blockchain. Their interaction is conditional, based on the nature of the user's input token:
-
OktoSettlementContract:
- The primary contract managing the state and logic of cross-chain intents according to ERC-7683.
- It Validates intents, processes fulfillment, handles final settlement, manages timeouts and refunds, logs progress through events, and controls permissions for different roles.
- Crucially, orders within the
OktoSettlementContractare always raised with an input token that is a "filler-supported token."
-
EscrowContract:
- Acts as a secure holding area for user funds during the transaction.
- It securely locks user assets upon intent initiation, releases assets to the fulfilling Filler only upon successful verification, enforces refund logic if deadlines are breached, and may use standards like Permit2 for secure token approvals via user signatures.
- The
EscrowContractis utilized specifically when the user's initial input token is not a "filler-supported token."
Interaction Flow based on Input Token Type:
Scenario 1: User's input token IS a "filler-supported token."
- The
EscrowContractis not used for the initial user funds. - The intent is registered, and the order in the
OktoSettlementContractwill directly reflect the user as the source and their filler-supported token as the input.
Scenario 2: User's input token IS NOT a "filler-supported token."
- An initial step first swaps the user's unsupported token into a filler-supported token.
- The resulting filler-supported tokens are then transferred to and held by the
EscrowContract. - An order is subsequently raised in the
OktoSettlementContract. In this order:- The
EscrowContractacts as the effective "user" or source of the input assets. - The input token specified in the order is the filler-supported token (which was the output of the initial swap).
- The funds remain securely in the
EscrowContractuntil a Filler accepts/opens the order in theOktoSettlementContract, at which point they are committed to the fulfillment and settlement process.
- The
This distinction ensures that the OktoSettlementContract consistently deals with a known set of supported tokens, simplifying its logic, while the EscrowContract provides the necessary interim custody when pre-processing (like an initial swap) is required for unsupported input tokens.
Off-Chain Components
These services and actors operate outside the blockchain but interact with the on-chain contracts:
-
Facilitator Node:
- An off-chain service that coordinates intents and Fillers.
- It receives signed user intents, validates their structure, broadcasts them to registered Fillers, potentially matches intents based on efficiency, and tracks intent status. (Note: Currently operated by Okto).
-
Filler (Solver) Network:
- A network of independent (but currently permissioned/registered) off-chain actors acting as liquidity providers.
- It monitors the Facilitator for intents they can fulfill profitably. It executes the necessary on-chain transactions to fulfill the intent, providing the required assets on the destination chain.
-
Settler Network:
- A network of independent off-chain actors responsible for verifying fulfillment.
- It monitors blockchains for fulfillment events. It checks if the fulfillment details match the original user intent. If valid, it triggers the final settlement step on the source chain contract, allowing the Filler to receive their compensation. (Note: Currently operated by Okto).
ULL vs. Trade Service
For developers using Okto, it's important to understand the relationship between ULL and the Trade Service:
-
ULL (Unified Liquidity Layer): Is the foundational engine for executing and settling cross-chain intents. It includes the core contracts and network actors (Fillers, Settlers). Direct interaction is typically managed by higher-level systems.
-
Okto Trade Service: Is the service layer built on top of ULL, providing developers with:
- A user-friendly API and SDK.
- Intelligent Routing (Pathfinder) that determines the best execution path (potentially combining ULL with other methods like DEX aggregators).
- Integration with DEX Aggregators for wider token support.
- Additional features like Risk Management.
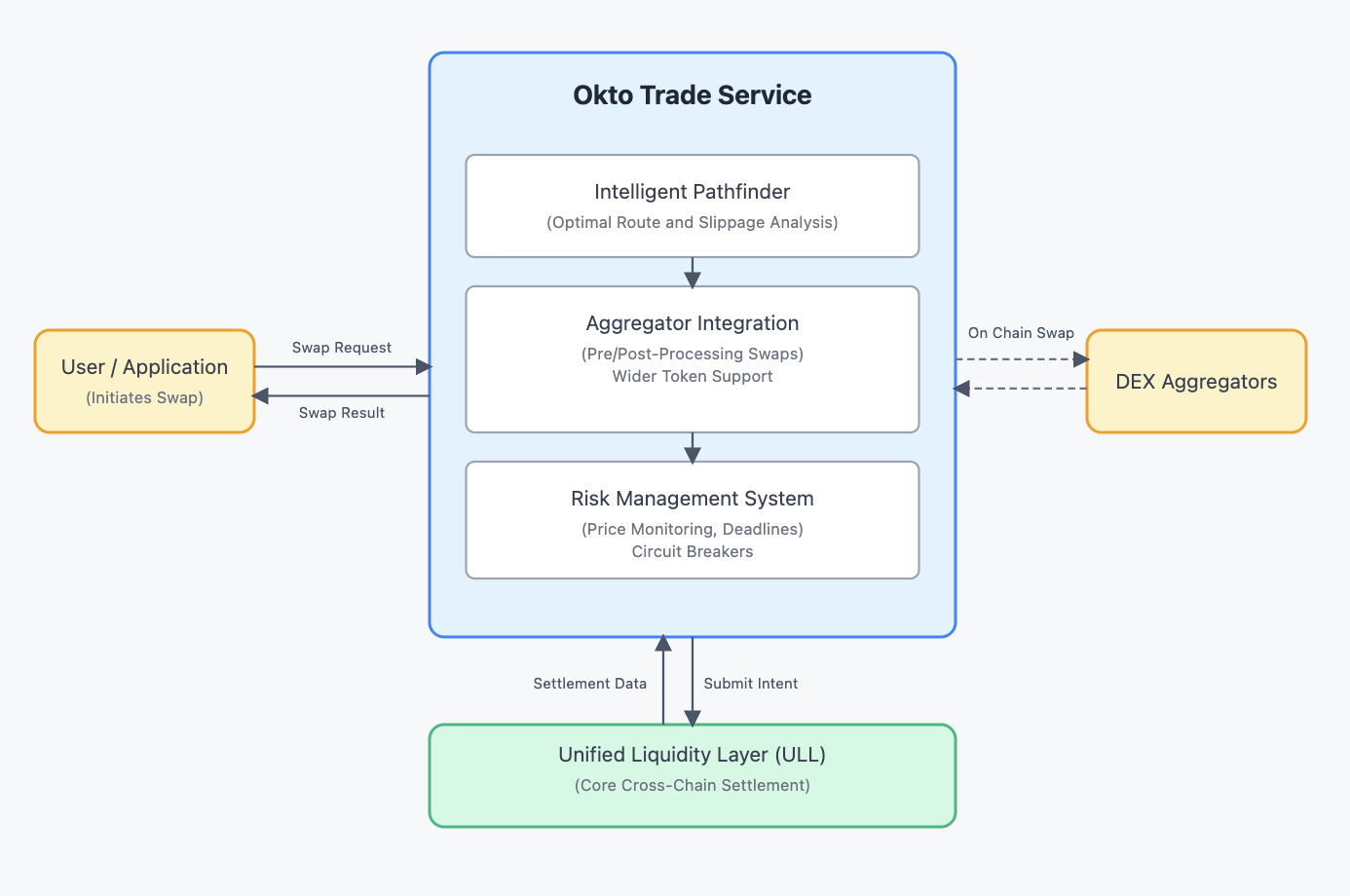
Developers typically integrate with the Okto Trade Service, which utilizes ULL's power under the hood. For more details, consult the Trade Service Documentation.
Benefits
- Simplified Integration: Provides a single interface for complex cross-chain swaps, eliminating the need to integrate with multiple protocols.
- Optimal Execution: Automatically finds and executes the most efficient swap routes based on cost, speed, and security preferences.
- Broad Token Coverage: Access swaps for a vast range of tokens via integrated aggregators and liquidity sources.
- Enhanced User Experience: Offers users a simple "one-click" experience for cross-chain swaps without requiring deep technical knowledge.
- Reliable Infrastructure: Built on proven standards with robust error handling and recovery mechanisms.
Getting Started
Ready to leverage ULL's powerful cross-chain capabilities?
- Explore Trade Service →: Access ULL through developer-friendly APIs
- Learn about Cross-Chain Intents →: Understand the ERC-7683 standard implementation
Decentralized Transaction Network (DTN)
Previous Page
Embedded Wallets
Discover Okto's Embedded Wallets: self-custodial wallets seamlessly integrated into your application via the Okto SDK. Learn how Wallet Providers define distinct ecosystems and control interoperability for enhanced user experience and security.