Architecture
Detailed breakdown of the Okto architecture and its core components
What is the Okto Platform?
The Okto Platform is a comprehensive wallet infrastructure designed to simplify how developers and users interact with blockchain technology. It abstracts away the complexities of multi-chain operations—managing wallets, bridging assets, paying gas fees, and handling fragmented liquidity—making blockchain applications more accessible for everyone.
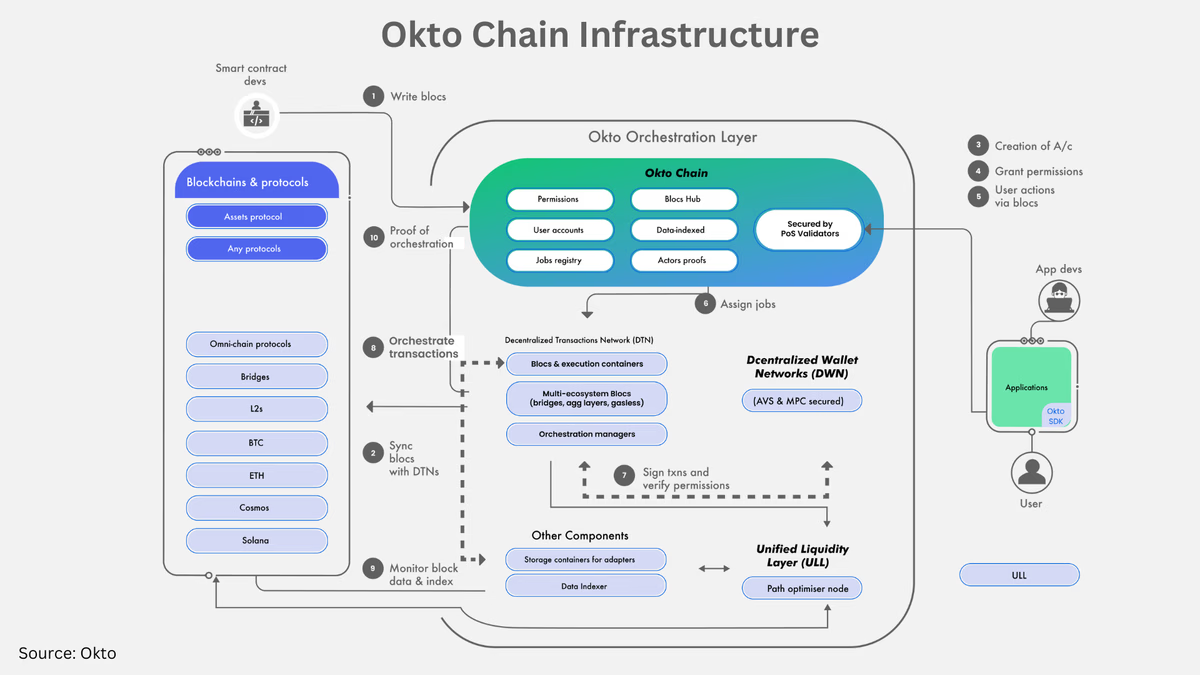
Core Components of the Okto Platform
The Okto Platform's architecture is built on four main interconnected components that work together to deliver a seamless blockchain experience:
1. Decentralized Wallet Networks (DWNs)
The Decentralized Wallet Network is at the core of Okto’s embedded wallet infrastructure and forms the foundation of simplified on-chain interactions. It enables users with a single embedded wallet for all major ecosystems - eliminating the complexity of cross-chain interactions at the source.
Key Features:
- Social Authentication: Users enjoy frictionless onboarding via Google, Email OTP, WhatsApp, etc. No seed phrases needed.
- Top-Grade Security: DWN uses delegated MPC (Multi-Party Computation) + TSS (Threshold Signature Scheme) technology, with EigenLayer AVS (Actively Validated Services) operators to securely manage wallet keys. Comprehensive audits back this security.
- Cross-Ecosystem Compatibility: One wallet interface for EVM, Solana, Aptos, and more.
- Delegated Transaction Flows: Users can approve batches of actions or grant temporary access to apps with programmable guardrails, enabling seamless experiences like session-based permissions without compromising security.
- Treasury Management: Provides enterprise-ready wallet functionality with automated, policy-controlled features.
2. Unified Liquidity Layer (ULL)
The ULL addresses liquidity fragmentation across the Web3 landscape by acting as an "aggregator of aggregators." It routes cross-chain swaps and transfers through the most efficient and cost-effective pathways available, using an intent-based approach powered by the ERC-7683 standard.
Key Features:
- Seamless cross-chain swaps: Move assets between any supported blockchains with one click - any to any token from any to any chain
- Optimal Path Routing: Automatically find the best path for your transactions based on cost, speed, and security preferences
- Pre-Loaded Liquidity: Enables immediate transaction capability without manual DEX integrations by developers.
- Unified Token Standards: Allows interaction with ERC-20, SPL, and other token standards through one consistent interface.
3. Decentralized Transaction Networks (DTNs)
The DTN serves as the "brain" of the Okto Platform, orchestrating complex multi-chain operations by translating user-defined intents into actionable sub-transactions across multiple blockchains. Users define outcomes (e.g., 'buy NFT X with ETH'); Okto's DTN bundles all cross-chain steps automatically.
Key Features:
- Transaction Bundling: DTN converts complex multi-step processes into one-click, signless actions.
- Cross-Chain Execution: Enables users to swap tokens, mint NFTs, and bridge assets across chains - all from a unified interface, driven by their intent-driven goals.
- Smart Intent Routing: Users declare goals; Okto’s DTN handles the technical execution, orchestrating subtasks and managing chain-specific details.
- Gasless Transactions: Facilitates fee payments in stablecoins or allows apps to sponsor gas entirely.
- MEV Protection: Incorporates built-in safeguards against front-running and sandwich attacks.
- Automatic Recovery: Intelligently retries failed transactions due to network congestion or other issues without requiring user intervention.
4. The Okto Chain
The Okto Chain serves as the central coordination platform for the entire Okto ecosystem. Built as a ZK-based Layer 2 on Polygon CDK, it ensures transparency, decentralization, and efficient task management across DWNs, ULLs, and DTNs.
Key Features:
- ZK-Powered Verification: Provides cryptographic proof of cross-chain transaction integrity.
- EigenLayer Security: Enhances protection through restaking mechanisms.
- Immutable Policy Enforcement & Ledger: Records user intents and DTN execution details as immutable records, ensuring trustless execution of security rules, user permissions, and compliance controls.
- Cross-Chain Coordination: Synchronizes and records activities across the DWN, ULL, and DTN for auditing, transparency, and triggering tasks via event emission.
Learn more about the Okto Chain →
How It All Works Together
The four components of the Okto Platform work in seamless coordination:
- User Intent: A user expresses a desired outcome (e.g., "stake ETH from my USDC on Polygon")
- DWN Authentication: The user authenticates via social login, with DWN managing secure wallet creation and session management
- Okto Chain Recording: The intent is recorded as a "job" on the Okto Chain for transparency and auditability
- DTN Orchestration: DTN picks up the job, breaks it into sub-transactions (bridge USDC, swap for ETH, stake ETH)
- ULL Routing: For liquidity-intensive steps, DTN coordinates with ULL to find optimal paths
- DWN Signing: All transaction payloads are securely signed by the DWN's MPC network
- Execution & Monitoring: DTN broadcasts transactions, monitors completion, and updates the Okto Chain
- Completion: The user's intent is fulfilled seamlessly across multiple chains
Benefits of the Okto Platform
1. For Developers:
- Rapid Integration: Build cross-chain features in days, not months.
- Chain-Agnostic Development: Write once, deploy everywhere with unified APIs.
- Simplified Architecture: Focus on application logic instead of blockchain complexity.
2. For Users:
- Web2-Like Experience: Login with familiar accounts, transact across any blockchain with one-click interactions.
- No Technical Complexity: Never manage private keys or worry about gas tokens.
- Unified Portfolio: View and manage assets across all chains from a single interface.
3. For Enterprises:
- Institutional Security: Military-grade protection with comprehensive audits.
- Policy Controls: Programmable transaction rules and compliance enforcement.
- Transparent Operations: Immutable audit trails for all cross-chain activities.
Wallet Provider / Client / User
In the Okto documentation, you'll frequently encounter three main personas: Wallet Provider(WP), Client, and User. These personas are key to navigating how Okto interacts with developers and users across its platform. Let's break down each of these roles to understand their place in the ecosystem.
Okto Chain
Next Page