Swap Scenarios
Explore the Trade Service swap scenarios including same-chain swaps and various cross-chain swap flows.
This page outlines all supported swap flows within the Okto Trade Service, including both same-chain and cross-chain scenarios. Each swap operation is executed via a sequence of on-chain transactions, some of which may involve routing, cross-chain transfers, or intermediate conversions. These steps are abstracted from the end-user to ensure seamless and secure execution.
Understand FST and Non-FST Tokens
- FST (Filler Supported Tokens): Tokens natively supported by the ULL (Unified Liquidity Layer) and eligible for direct cross-chain transfers.
- Non-FST (Filler Unsupported Tokens): Tokens not supported by ULL for cross-chain transfers. These must be first converted to an FST before moving across chains.
For more details, check the Supported Networks & Tokens guide.
1. Same Chain Swap (Any Token → Any Token)
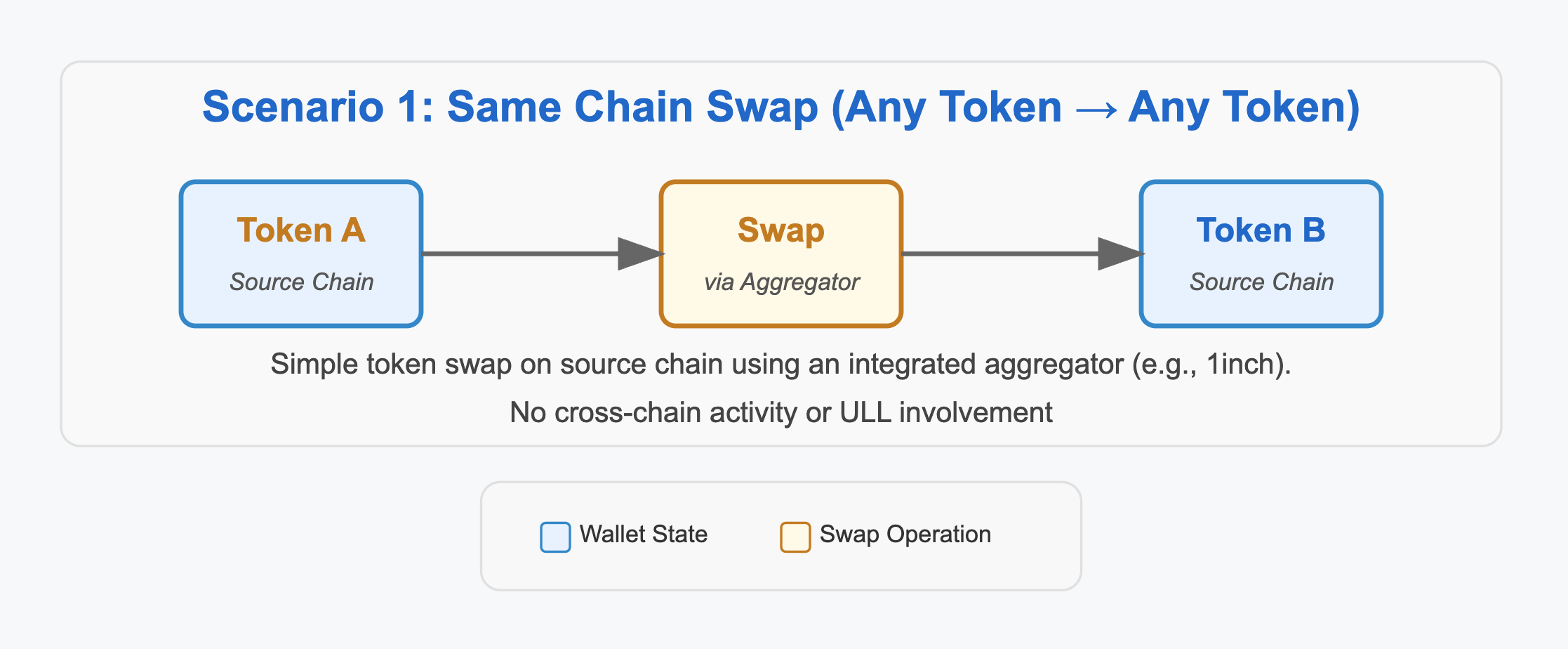
This is an intra-chain swap, where both the source and destination tokens exist on the same blockchain. The transaction is performed within the user's wallet address and does not involve any cross-chain messaging or transfers.
Example- Swap WETH (Any Token) to USDT (Any Token) on the Base network.
2. Pure Cross-Chain Bridge (FST → FST)
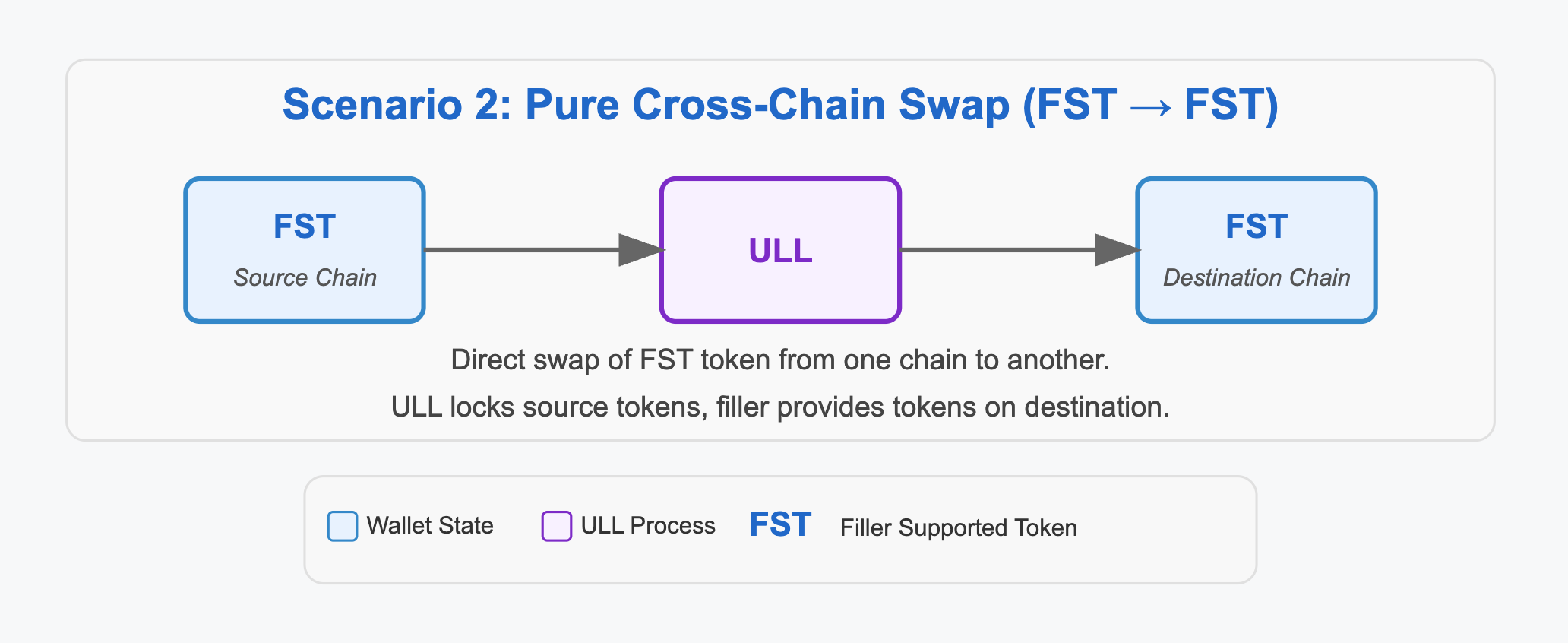
In this scenario, a supported FST token is transferred from the source chain to the destination chain. Both source and destination tokens must be FSTs.
Example- Swap USDC (FST) on BSC to USDC (FST) on Ethereum.
3. Cross-chain + Destination Swap (FST → Non-FST)
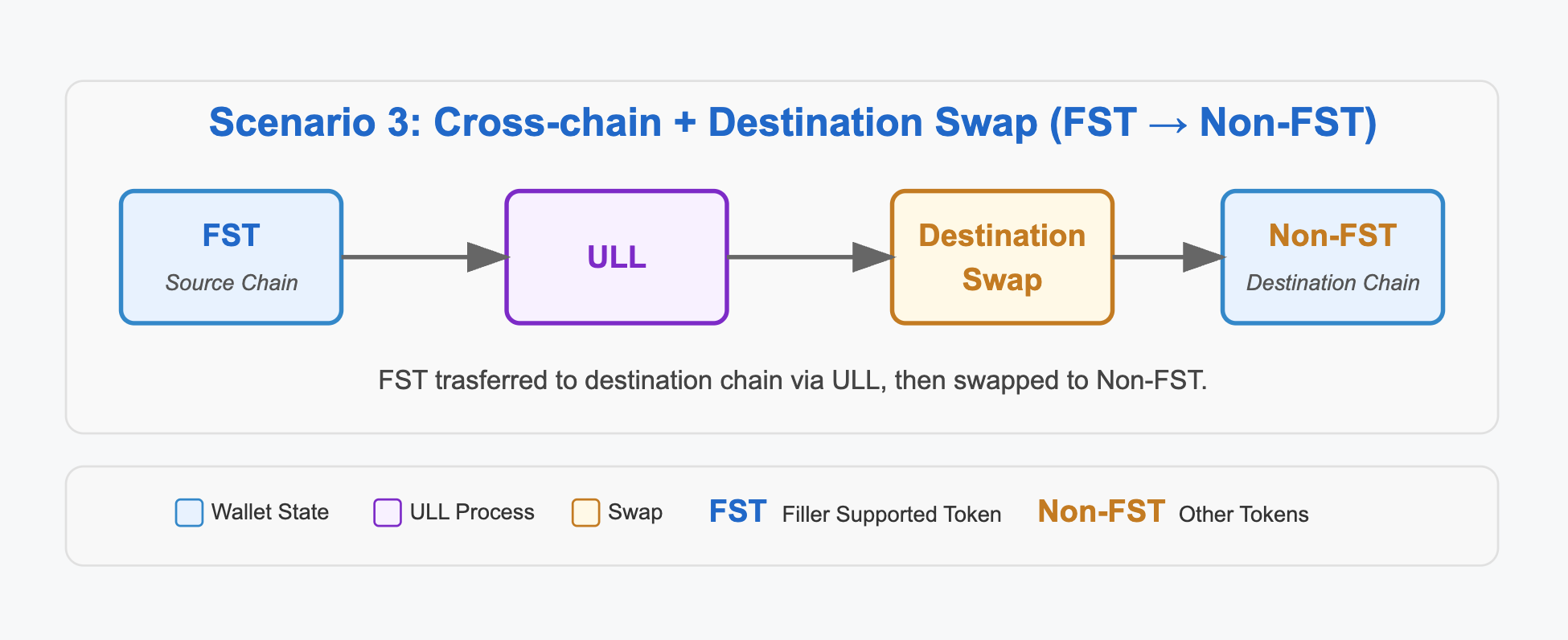
This scenario begins with a FST on the source chain, allowing direct cross-chain transfer via ULL. After the token is transferred to the destination chain, it is then swapped into a Non-FST using a same-chain swap.
Example- Swap USDC on BSC (FST) to ETH on Ethereum (Non-FST).
4. Source Swap + Cross-chain (Non-FST → FST)
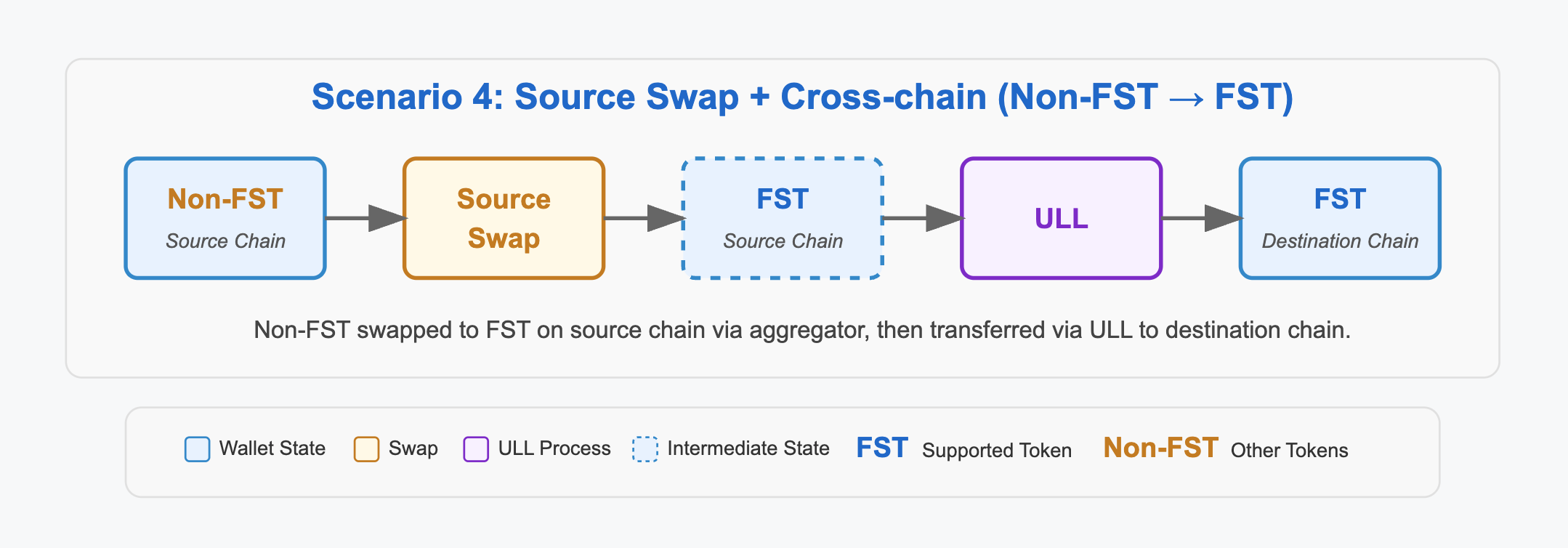
In this scenario, the user starts with a Non-FST on the source chain. Because Non-FST tokens cannot be directly transferred across chains, the system first converts it to a FST using a same-chain swap. The resulting FST is then moved to the destination chain.
Example: Swap ETH (Non-FST) on Ethereum to USDC (FST) on Base.
5. Source Swap + Cross-chain + Destination Swap (Non-FST → Non-FST)
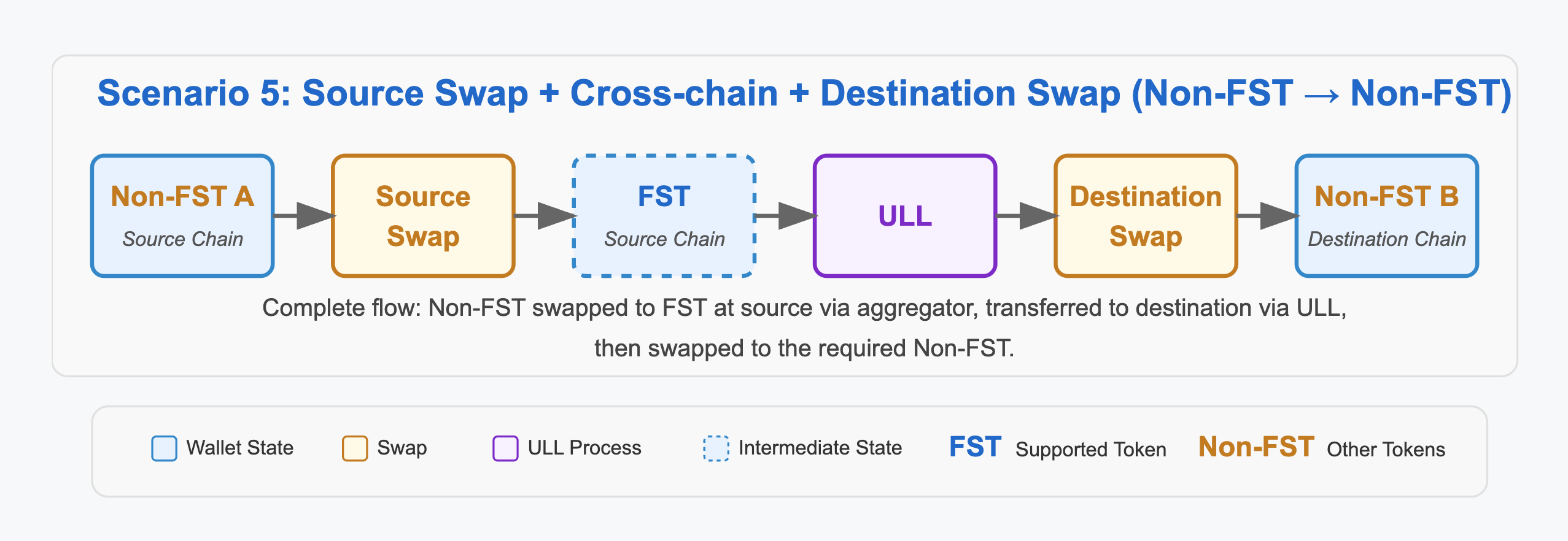
This is the most comprehensive swap flow, involving a Non-FST on both the source and destination chains. The source Non-FST is first converted to an FST, then transferred across chains, and finally swapped again to the target Non-FST.
Example: Swap ETH (Non-FST) on Ethereum to SHIBA (Non-FST) on BSC.